Have a question about using WolframAlpha?Simple transformation for y=f(x) functionGraph f(x)=(x2)^21 Find the properties of the given parabola Tap for more steps Use the vertex form, , to determine the values of , , and Since the value of is positive, the parabola opens up Opens Up Find the vertex Find , the distance from the vertex to the focus Tap for more steps

Let F Be A Function Defined By F X X 1 2 1 Xge1 S
F(x)=x^2+1 domain and range
F(x)=x^2+1 domain and range-Jan 28, · Ex 12, 10 Let A = R − {3} and B = R − {1} Consider the function f A → B defined by f (x) = ((x − 2)/(x − 3)) Is f oneone and onto?The Function which squares a number and adds on a 3, can be written as f (x) = x2 5 The same notion may also be used to show how a function affects particular values Example f (4) = 4 2 5 =21, f (10) = (10) 2 5 = 105 or alternatively f x → x2 5 The phrase "y is a function of x" means that the value of y depends upon the value of




Use The Graph That Shows The Solution F X G X F X X 2 4x 2 G X 1 2 2 1 What Is The Brainly Com
The vertical asymptote is x = 4 The oblique asymptote is y = 3 x 1 4 No horizontal asymptote Explanation Let f (x) = x − 4 3 x 2 2 x − 5 More Items ShareWolframAlpha answers specific questions rather than explaining general topics (eg Enter "2 cups of sugar", not "nutrition information") You can only get answers about objective facts (eg Try "highest mountain", not "most beautiful painting")Mar 11, 21 · Transcript Ex 55, 16 Find the derivative of the function given by f (𝑥) = (1 𝑥) (1 𝑥^2) (1 𝑥^4) (1 𝑥8) and hence find f ′(1) Given 𝑓(𝑥)=(1𝑥)(1𝑥^2 )(1𝑥^4 )(1𝑥^8 )" " Let 𝑦=(1𝑥)(1𝑥^2 )(1𝑥^4 )(1𝑥^8 ) Taking log both sides log 𝑦 = log (1𝑥)(1𝑥^2 )(1𝑥^4 )(1𝑥^8 ) log 𝑦 = log (1𝑥)log(1𝑥^2 )log(1
Divide f2, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac{f}{2}1 Then add the square of \frac{f}{2}1 to both sides of the equation This step makes the left hand side of the equation a perfect squareFree PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystepThen, f(x)g(x) = 4x 2 4x 1 = 1 Thus deg( f ⋅ g ) = 0 which is not greater than the degrees of f and g (which each had degree 1) Since the norm function is not defined for the zero element of the ring, we consider the degree of the polynomial f ( x ) = 0 to also be undefined so that it follows the rules of a norm in a Euclidean domain
Given f (x) = 3x 2 – x 4, find the simplified form of the following expression, and evaluate at h = 0 This isn't really a functionsoperations question, but something like this often arises in the functionsoperations contextThe function f is defined by f (x) = x4 −4x2 x 1 for −5 ≤ x ≤ 5 What is the interval in which the minimum of value of f Purely a graphical approximation;The question seems rather odd Explanation The formula for computing the surface area is S = 2 π ∫ f (x) 1 (f ′ (x)) 2
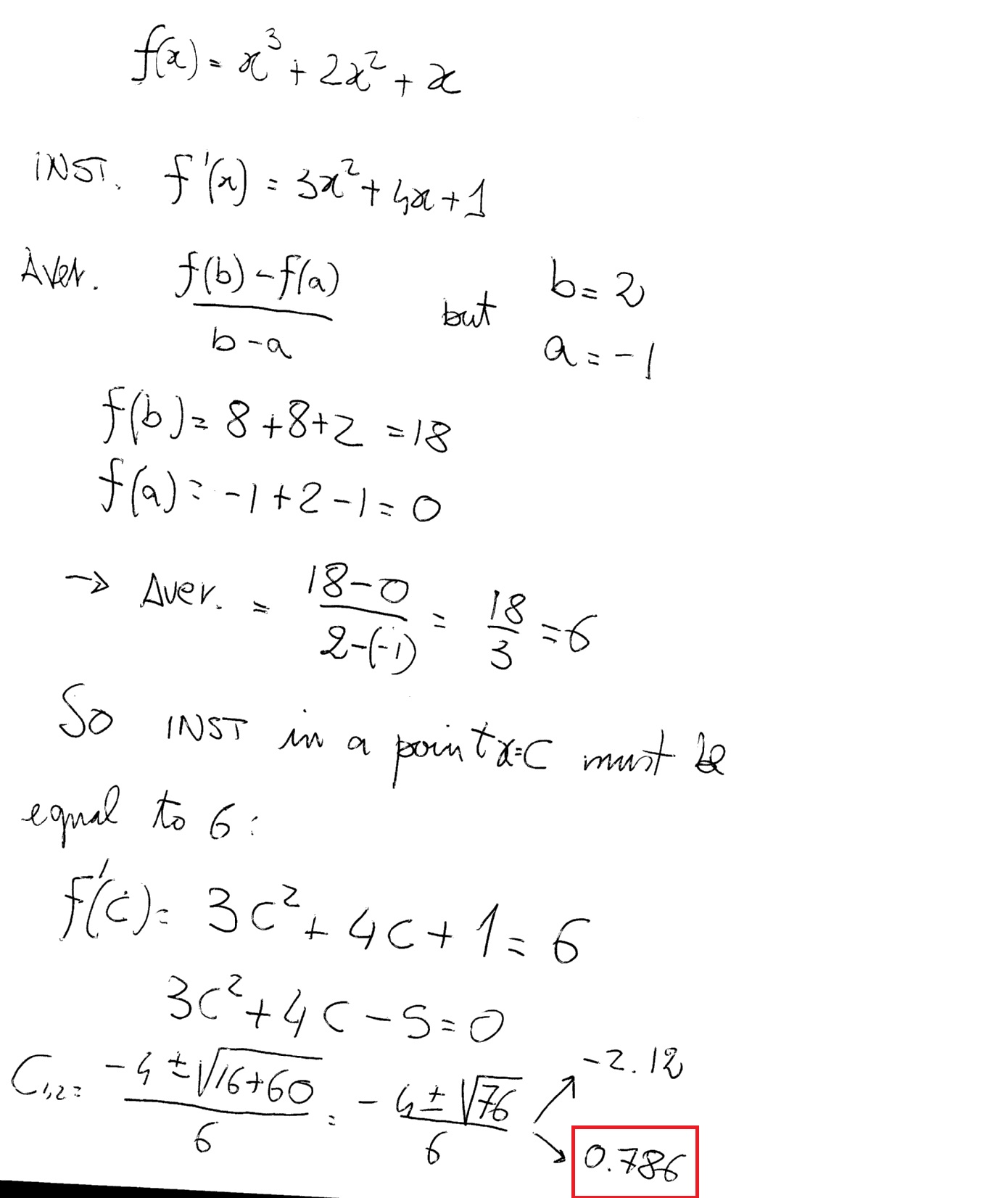



If F Is Defined By F X X 3 2x 2 X How Do You Find The Value Of X When The Average Rate Of Change Of F On The Interval X 1 To X




Given That G X 3x 2 2x 1 Find Each Of The Following A G 0 B G 1 C G 3 D G X Brainly Com
Calculus We find the Maclaurin series for f(x) = 1/(1x)^2 as 1 2x 3x^2 by using three different methods (a) Derivative of power series, (b)Mar , 18 · (oo, 1) uu 0, oo) Given f(x) = x^2/(1x^2) Let y = f(x) and attempt to solve for x y = f(x) = x^2/(1x^2) = (1(1x^2))/(1x^2) = 1/(1x^2)1 Add 1 to both ends to get y 1 = 1/(1x^2) Multiply both sides by (1x^2)/(y1) to get 1x^2 = 1/(y1) Add x^21/(y1) to both sides to get 11/(y1) = x^2 In order for this to have a real valued solution, we require 11/(y1) >= 0 That is yIn this *improvised* video, I show that if is a function such that f(xy) = f(x)f(y) and f'(0) exists, then f must either be e^(cx) or the zero function It'
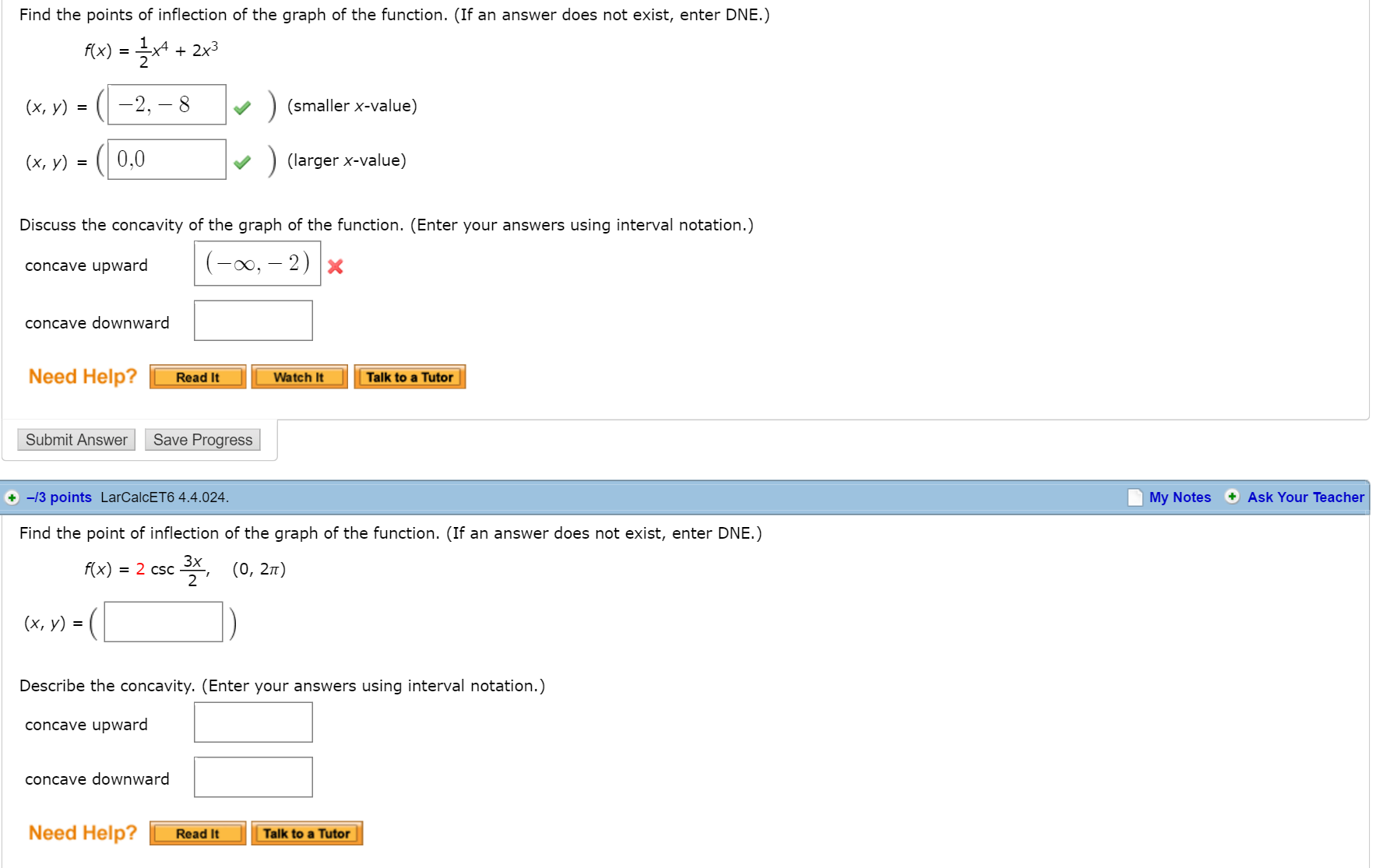



Find The Points Of Inflection Of The Graph Of The Chegg Com




How To Graph A Quadratic Equation 10 Steps With Pictures
Suppose you are given the two functions f (x) = 2x 3 and g(x) = –x 2 5Composition means that you can plug g(x) into f (x)This is written as "(f o g)(x)", which is pronounced as "fcomposeg of x"And "( f o g)(x)" means "f (g(x))"That is, you plug something in for x, then you plug that value into g, simplify, and then plug the result into fSteps for Solving Linear Equation f ( x ) = 1 \frac { 2 } { x 1 } , s f ( x) = 1 − x 1 2 , s Multiply both sides of the equation by x1 Multiply both sides of the equation by x 1 fx\left (x1\right)=x12 f x ( x 1) = x 1 − 2 Use the distributive property to multiply fx by x1Div {x^2 y^2, y^2 x^2} manipulate c in x^2 y^2 = c;




F X 2 X 3 X 2 Zonealarm Results




Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X 1 1 X 2 X I
Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the yvalue g(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history




If The Function F X X 2 1 X 1 When X Ne1 K Whe




Let F X X 1 X 1 Then F Is Differentiable In Youtube
Apr 06, 18 · The domain of f (x) is x ∈ R To determine the range, proceed as follows y = 1 1 x2 y(1 x2) = 1 y yx2 = 1 yx2 = 1 −y x2 = 1 − y y x = √ 1 − y y The range of f (x) is the domain of x//googl/JQ8NysDerivative of f(x) = 1/x Using the Limit DefinitionC < 0 moves it down
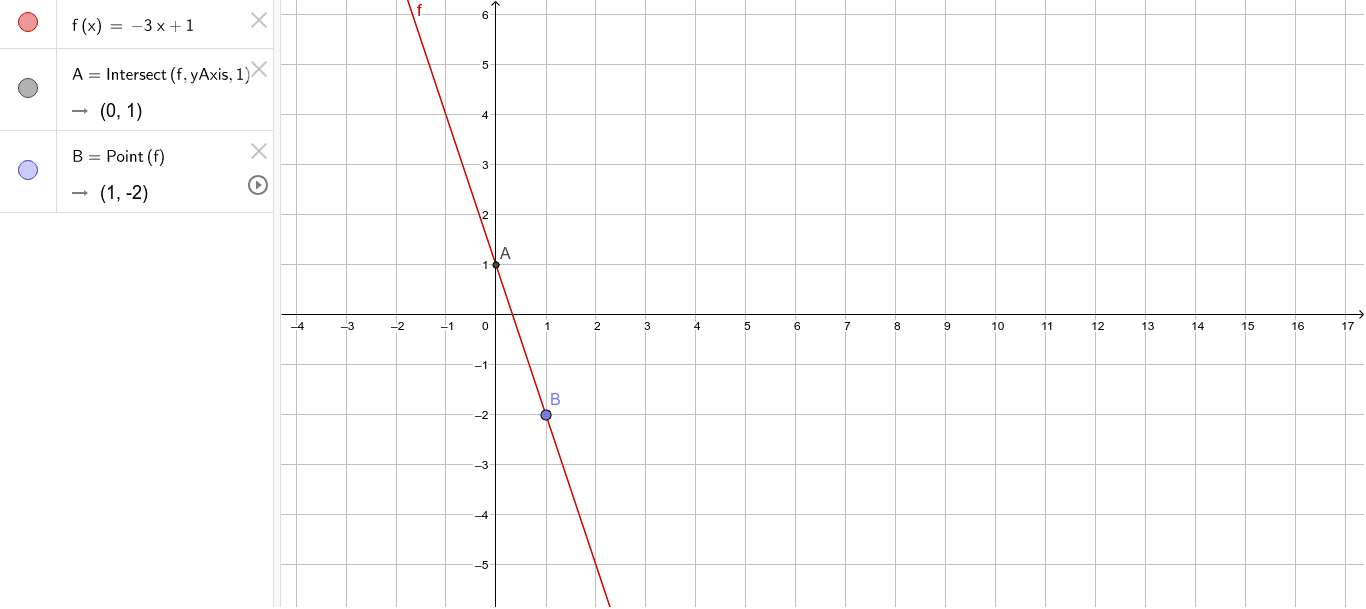



F X 3x 1 Geogebra




F R Gt R F X X 1 X 2 Determine Intervals In Which The Given Function Are Strictly Increasing Or Brainly In
Contact Pro Premium Expert Support »Hence, the name "piecewise" function When I evaluate it at various x values, I have to be careful to plug theIt function maps from the real numbers to the range (1,7/3 (1 to 7/3, excluding 1, including 7/3) This can be shown as follows Assume (x^2x2)/ (x^2x1) to be
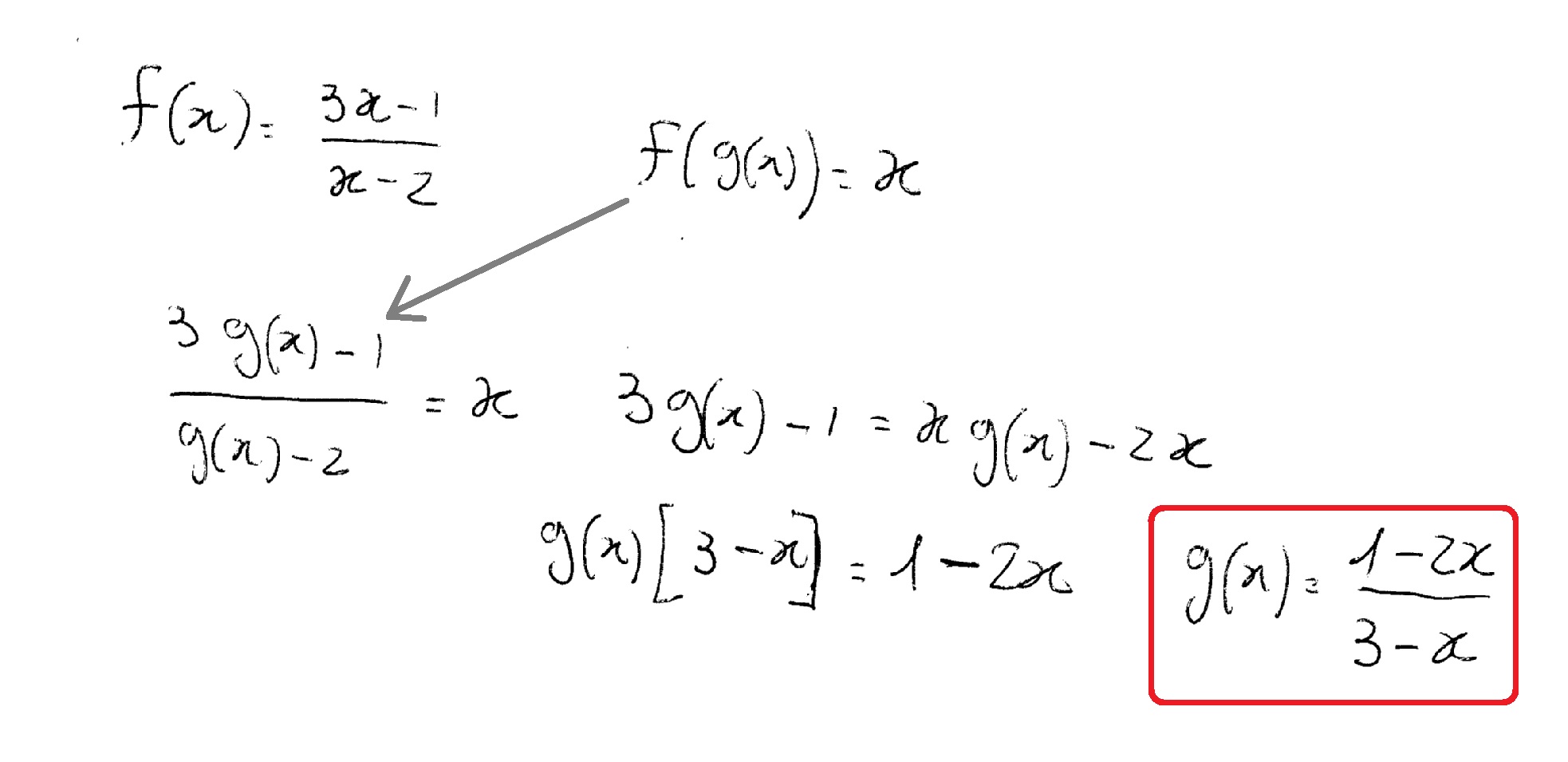



Let F X 3x 1 X 2 And F G X X How Do You Find G X Socratic




How To Solve This Problem On Application Of Derivative Mathematics Stack Exchange
58 Find roots (zeroes) of F(x) = x 6 x 4 x 3 x 2 1 See theory in step 42 In this case, the Leading Coefficient is 1 and the Trailing Constant is 12 Use ^(1/2) for square root ,'*' for multiplication, '/' for division, '' for addition, '' for subtraction Eg1 Write input √x as x^(1/2) 2 Write 5x as 5*x 3 Write x5 as x5 4 Write x 25x as x^25*x 3 Use paranthesis() while performing arithmetic operations Eg1 Write sinxcosxtanx as sin(x)cos(x)tan(x) 2 Write secx*tanxFor instance, when D is applied to the square function, x ↦ x 2, D outputs the doubling function x ↦ 2x, which we named f(x) This output function can then be evaluated to get f(1) = 2, f(2) = 4, and so on Higher derivatives Let f be a differentiable function, and let f ′ be its derivative




Misc 15 Let F X X2 X G X 2 X 1 2 1 Are F G




Find The Fourier Series Of The Function F X Of Chegg Com
Answer to Find the following using the table below X 1 2 3 3 4X^45x^24=0 \sqrt{x1}x=7 \left3x1\right=4 \log _2(x1)=\log _3(27) 3^x=9^{x5} equationcalculator f(g(2)), g(x)=2x1, f(x)=x^{2} en Related Symbolab blog posts High School Math Solutions – Quadratic Equations Calculator, Part 1 A quadratic equation is a second degree polynomial having the general form ax^2 bx c = 0, where a, bAug 15, · Find the domain and range of the real function f (x) = x/1x^2 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ ️Given real function is f (x) = x/1x^2 ️1 x^2 ≠ 0 ️x^2 ≠ 1 ️Domain x ∈ R




The Domain Of The Function F Given By F X X 2 2x 1 X 2 X
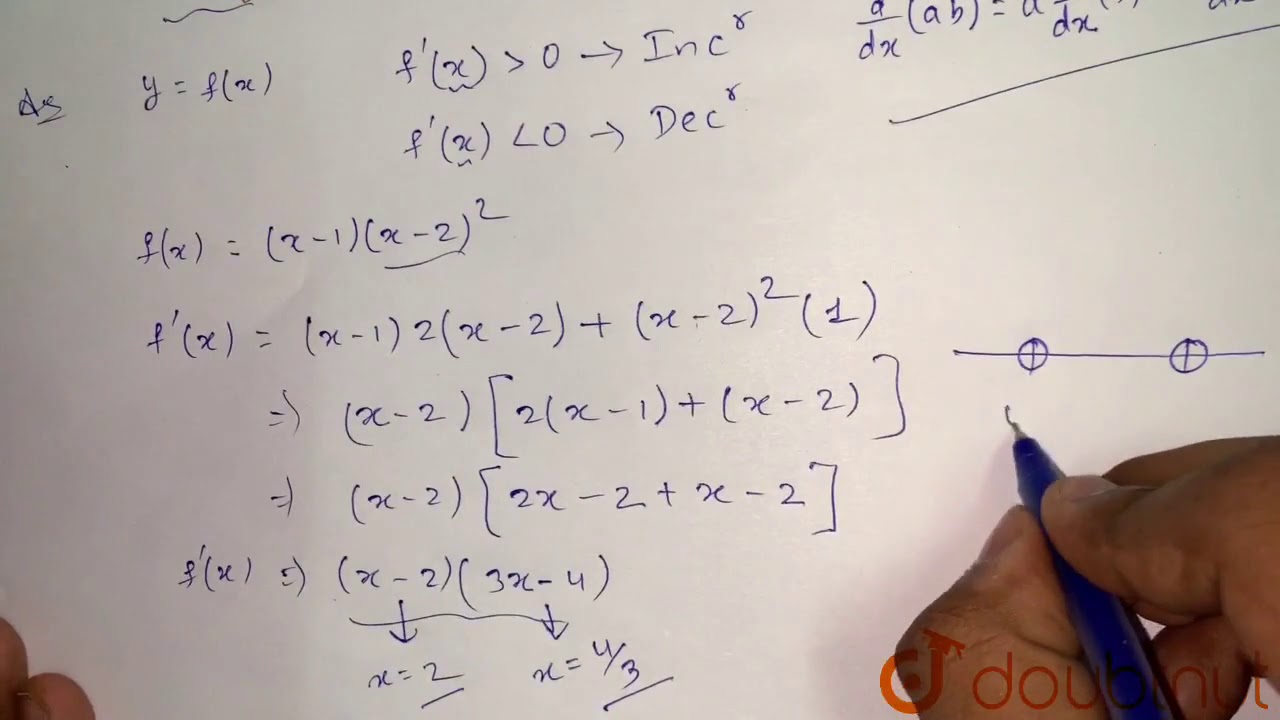



Find The Intervals In Which F X X 1 X 2 2 Is Increasing Or Decreasing Youtube
If f(x) g(x) = e − x where f(x) is an even function and g(x) is an odd function then f(x) = View solution Let u and v be two odd functions, then the function uov isAlgebra Find the Domain and Range f (x)= (1/2)^x f (x) = ( 1 2)x f ( x) = ( 1 2) x The domain of the expression is all real numbers except where the expression is undefined In this case, there is no real number that makes the expression undefined Interval NotationFree math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantly
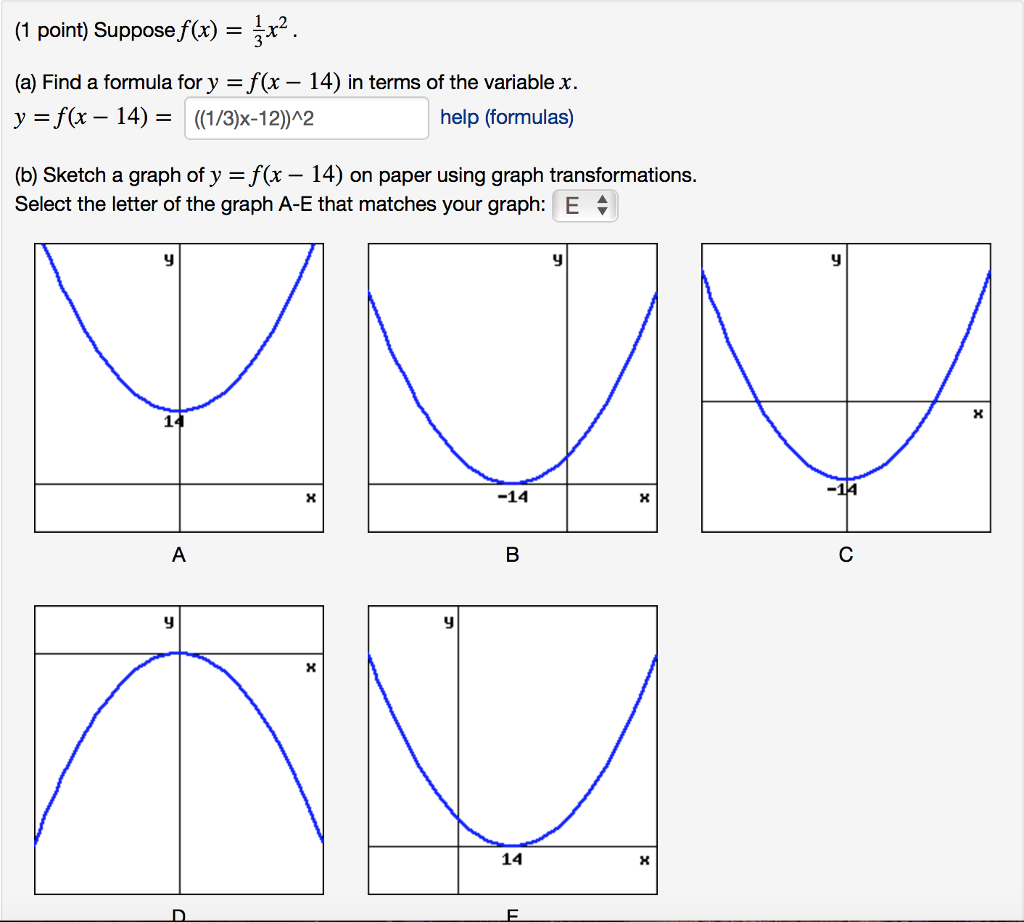



Suppose F X 1 3 X 2 A Find A Formula For Y Chegg Com
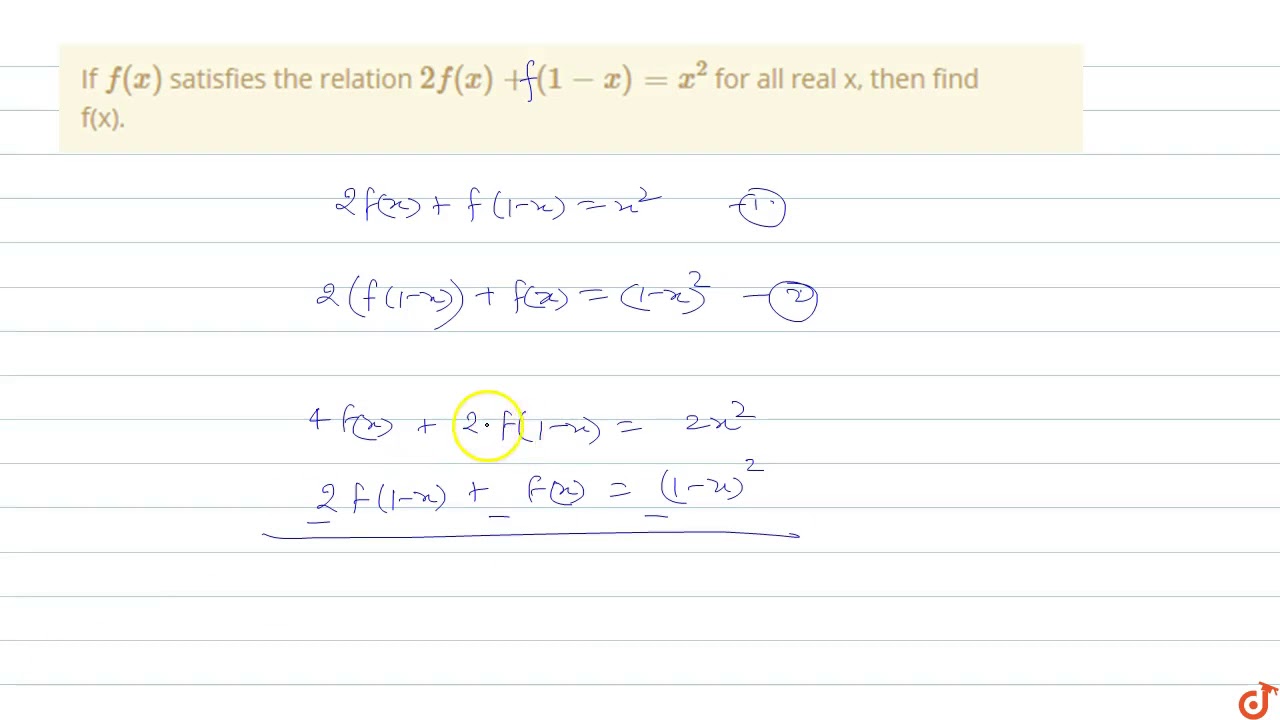



If F X Satisfies The Relation 2f X 1 X X 2 For All Real X Then Find F X Youtube
Graph f(x)=(x^21)/(x1) Rewrite the function as an equation Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is , where is the slope and is the yintercept Find the values of and using the formNov 25, 16 · lim_(x rarr 1)(x^21)/(x1) = 2 Let f(x) = (x^21)/(x1) then f(x) is defined everywhere except at x=1, however when we evaluate the limit we are not interested in the value of f(1), just the behaviour of f(c) for c close to 1Algebra Find the Domain and Range F (x)=1/ (x^2) F (x) = 1 x2 F ( x) = 1 x 2 Set the denominator in 1 x2 1 x 2 equal to 0 0 to find where the expression is undefined x2 = 0 x 2 = 0 Solve for x x Tap for more steps Take the square root of both sides of the equation to eliminate the exponent on the left side x = ± √ 0 x = ± 0
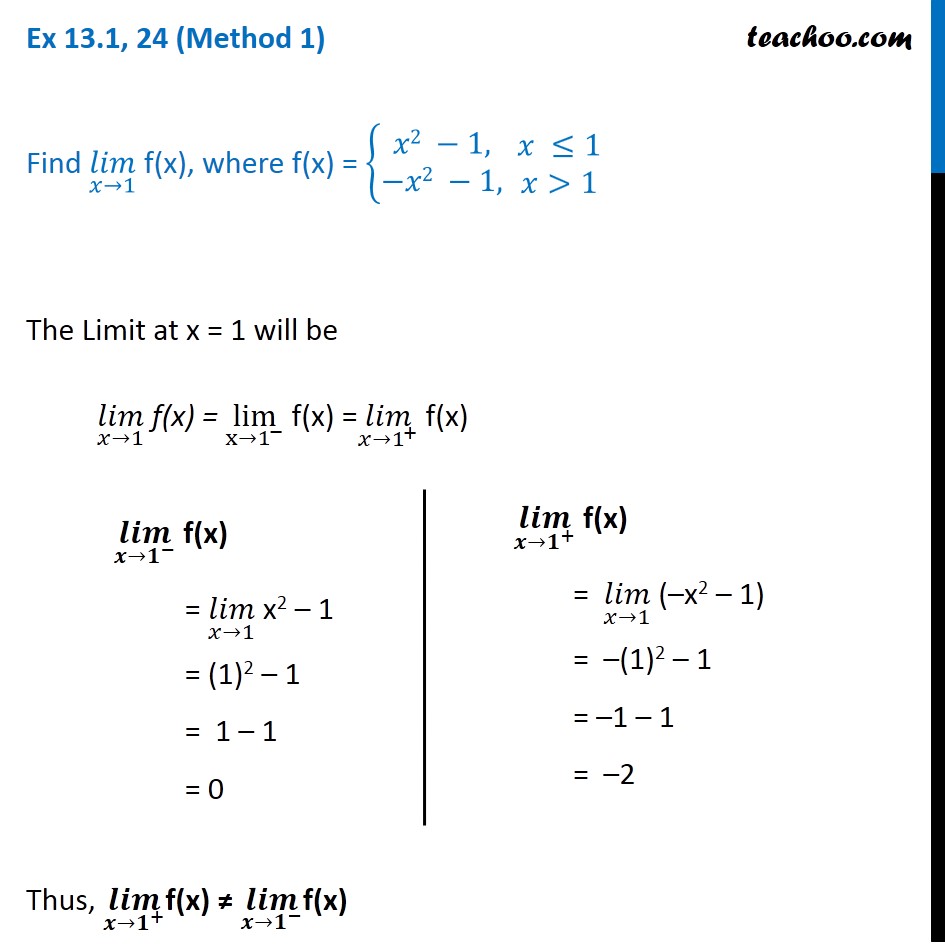



Ex 13 1 24 Find Lim X 1 Where F X X 2 1 X 1 X 2 1



How Do You Find An Equation Of The Tangent Line To The Graph F X X 2 2x X 1 At 1 6 Socratic
53 Factoring x2 x 1 The first term is, x2 its coefficient is 1 The middle term is, x its coefficient is 1 The last term, "the constant", is 1 Step1 Multiply the coefficient of the first term by the constant 1 • 1 = 1 Step2 Find two factors of 1 whose sum equals the coefficient of the middle term, which is 1Please Subscribe here, thank you!!!Minimum f = 463, nearly This is improved to 8sd, \displaystyle {} , using an iterative numerical method
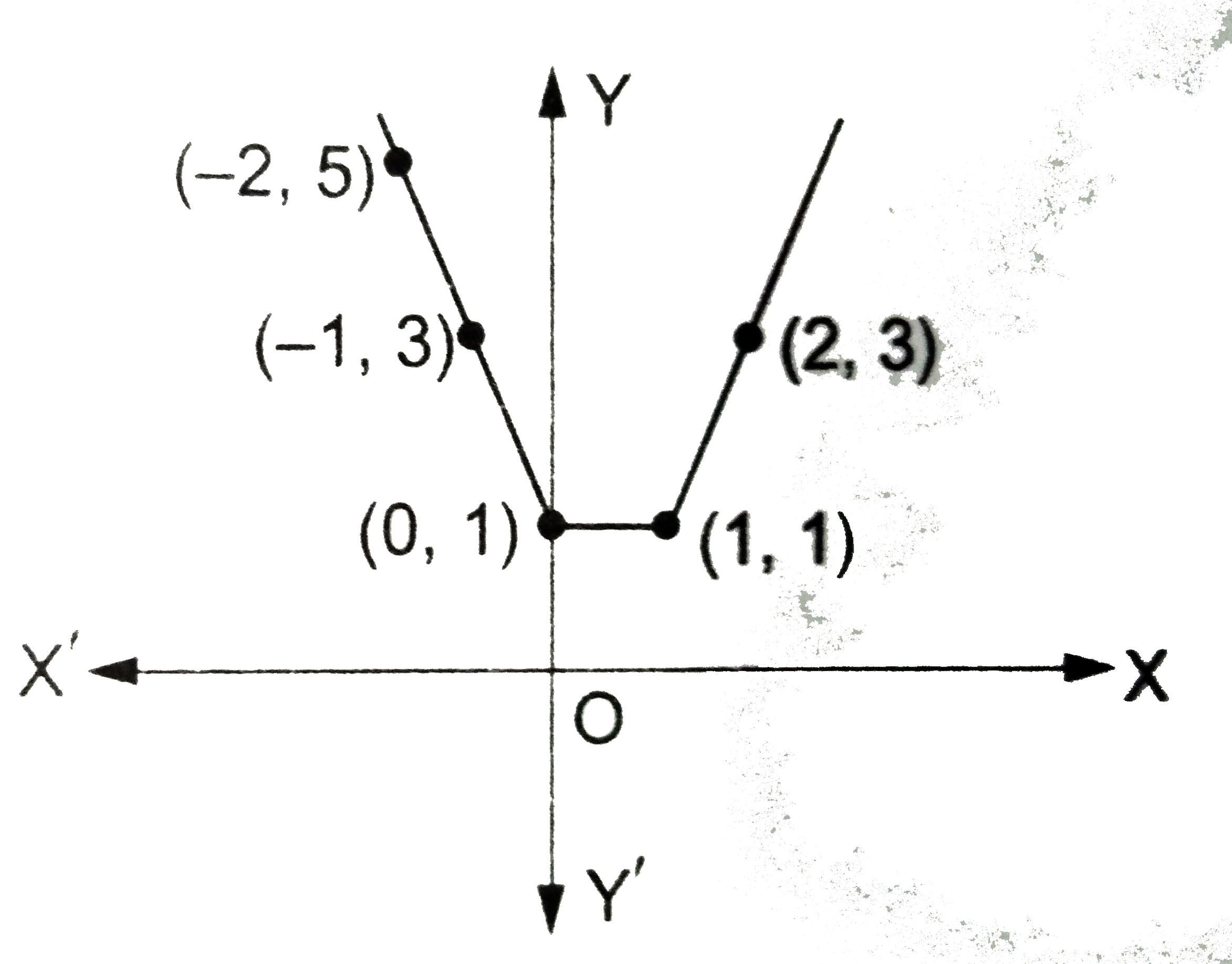



Draw The Graph Of The Function F X X X 1




Solved Obtain The Fourier Series Of F X 1 X 2 Over T Chegg Com
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyMar 12, 21 · Example 10 Discuss the continuity of the function f defined by 𝑓(𝑥)={ (&𝑥2, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥≤1@&𝑥−2, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥>1)┤ 𝑓(𝑥)={ (&𝑥2, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥≤1@&𝑥−2, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥>1)┤ Since we need to find continuity at of the function We check continuity for different values of x When x = 1 When x < 1 When x > 1 Case 1 WApr 15, 21 · Transcript Ex 65, 3 Find the local maxima and local minima, if any, of the following functions Find also the local maximum & the local minimum values, as the case may be (i) f (𝑥)=𝑥2 f(𝑥)=𝑥^2 Finding f'(x) f'(x) = 2x Putting f'(x) = 0 2x = 0 x = 0 Finding f''(x) f'(x) = 2x Differentiating again f''(x) = 2 Since f''(x) > 0 for x = 0 So, f(x) is minimum at x




The Domain Of The Function F X Sqrt X 1 X 3 X 2 Is 1




The Range Of The Function F X X 2 2x 2 Is
Given the function f (x) as defined above, evaluate the function at the following values x = –1, x = 3, and x = 1 This function comes in pieces;Answer to Find the critical points of f(x) = x2 1 / x2 1 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homeworkGraph f(x)=(x2)(x1)(x1) Find the point at Tap for more steps Replace the variable with in the expression Simplify the result Tap for more steps Simplify each term Tap for more steps Raising to any positive power yields Raising to any positive power yields Multiply by Multiply by




Misc 13 Find Points F X X 2 4 X 1 3 Has Local Maxima




If F 2 X F 1 X1 X X 3 X 1 1 F X 0 Then Find F 2 Where Is The G I F
Answer to (1 point) Find f if f"(x) = 2 cos(x), f(0) = 7, f(1/2) = 1 f(x) = (1 point) Find f if f'(x) = 4/V1 – x2 and f(1) =




If F Mathbb R Setminus 0 1 To Mathbb R Satisfies F X 2f Left Frac 1 X Right 3f Left Frac X X 1 Right X Then 8f 4 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Let F Be A Function Defined By F X X 1 2 1 Xge1 S
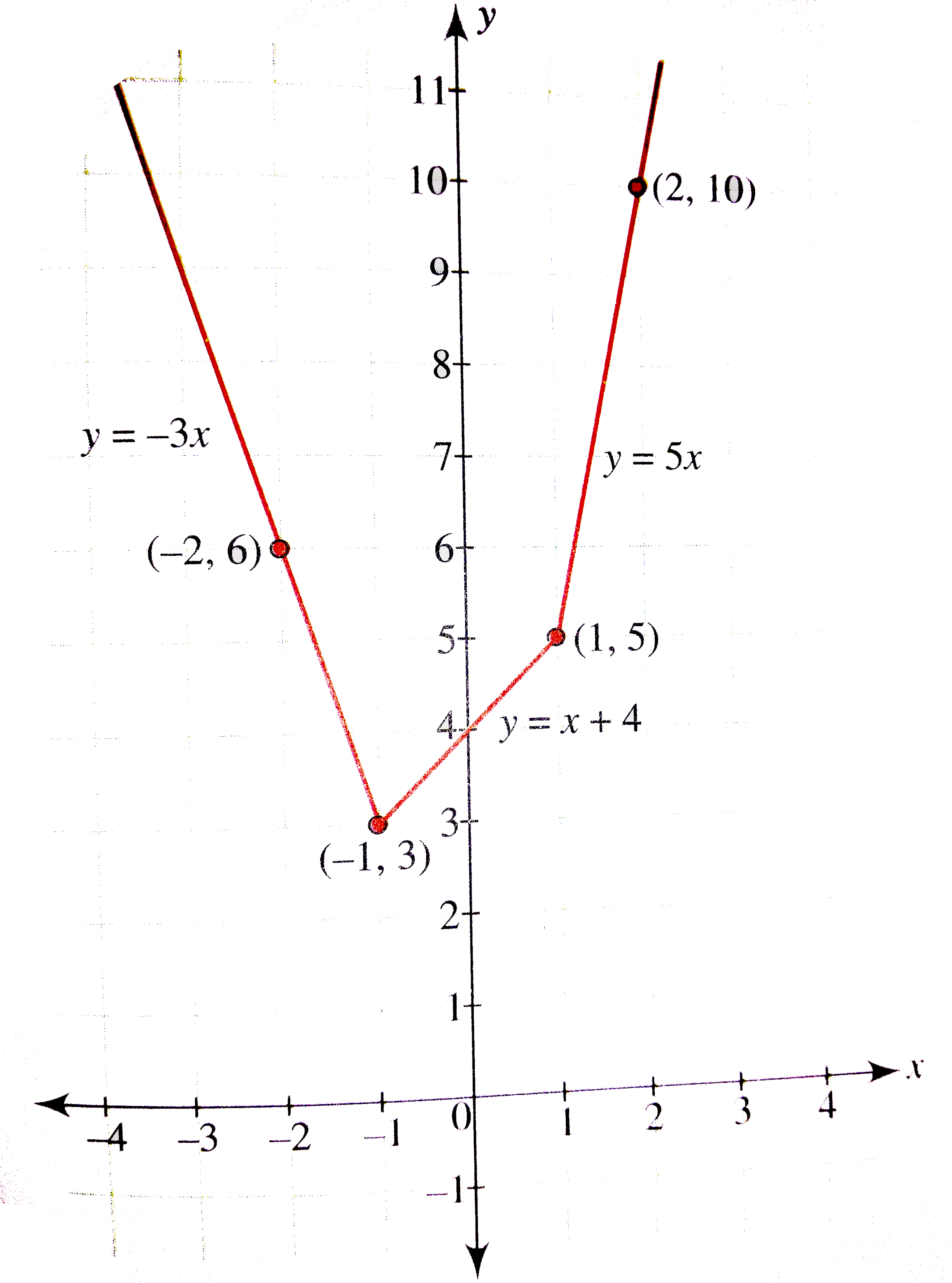



Let F X X 2 X 1 2 X 1 Find The Values Of K If F X K
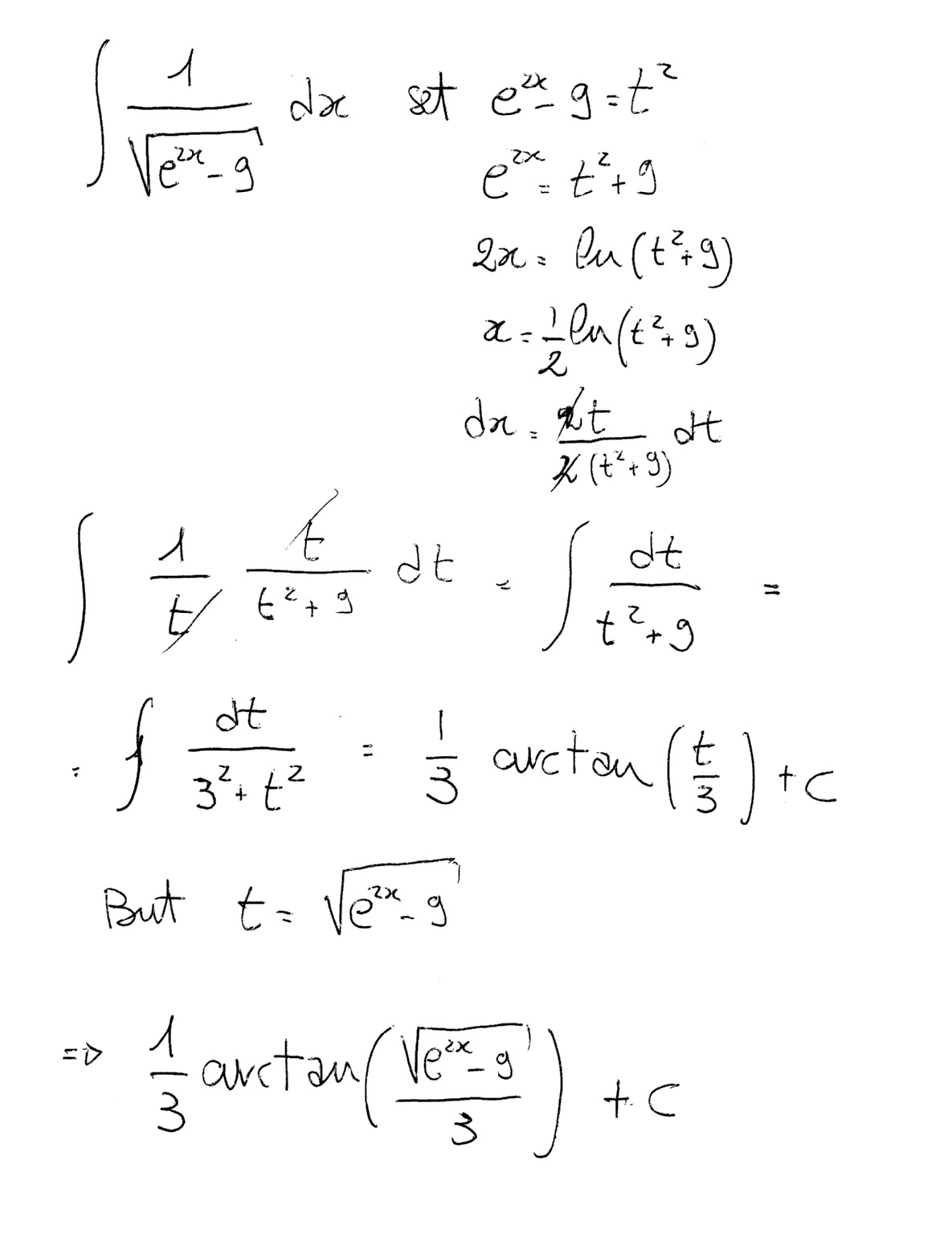



How Do I Find The Antiderivative Of F X 1 E 2x 9 1 2 Socratic




F X 3 Find The Numerical Value Of




Please Help For All Values Of X F X X 1 And G X 2x 2 3 Solve Fg X Gf X Brainly Com




Find The Domain And Range Of F X 1 Sqrt X 2




Ex 1 3 6 Show F X X X 2 Is One One Find Inverse Of F




Use The Graph That Shows The Solution F X G X F X X 2 4x 2 G X 1 2 2 1 What Is The Brainly Com




Misc 2 If F X X2 Find F 1 1 F 1 1 1 1 Chapter 2




If F X X 1 X 2 X 3 Then A Maximum Value Of F X Is 3 If X In 2 3 B Maximum Youtube




How Do You Differentiate F X 2x 1 X Socratic




The Range Of F X 2 X X 1 X X Where Denotes The Greatest Integer Function Is Youtube




Use Differentiation To Find A Power Series Chegg Com




If F X 1 2x 1 X 1 2 Then Show That F F X 2x 1 2x




If F X X 3x 1 Find Xer Such That F 2x F X Brainly In
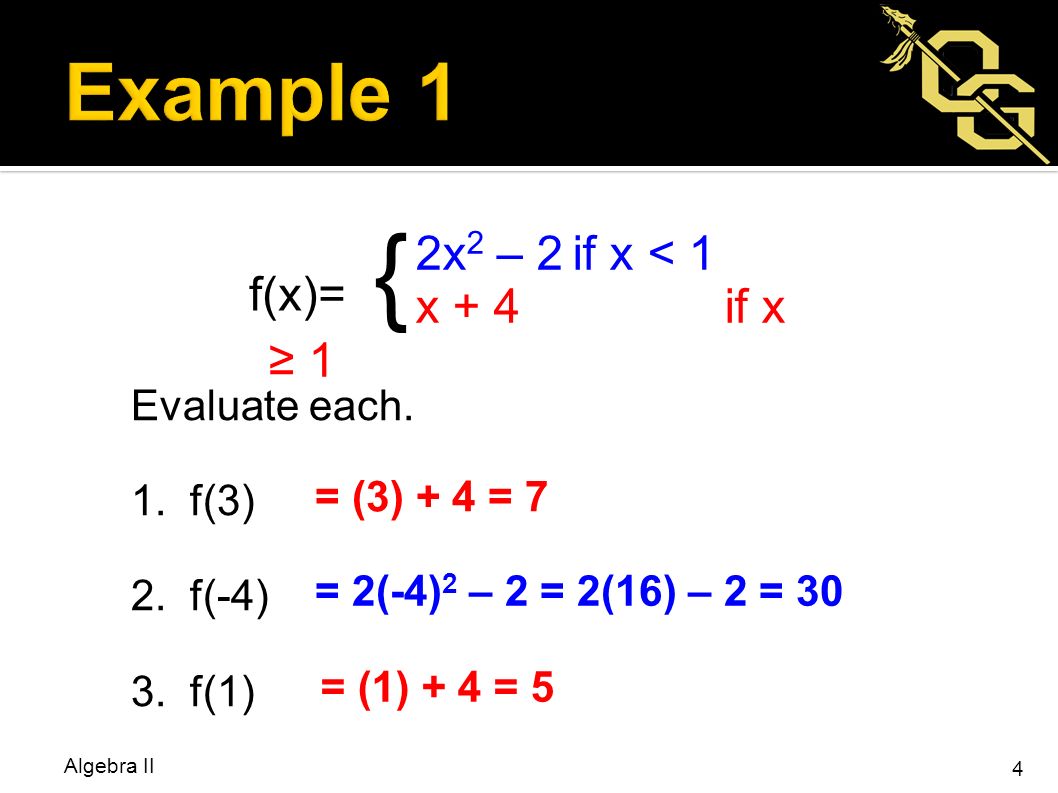



Bellwork Graph Each Line 1 3x Y 6 2 Y 1 2 X 3 Y Ppt Video Online Download




If F X 1 X 2 What Is F 3 H Brainly Com




What Is The Equation Of The Normal Line Of F X Sqrt X 1 X 2 3 At X 2 Socratic
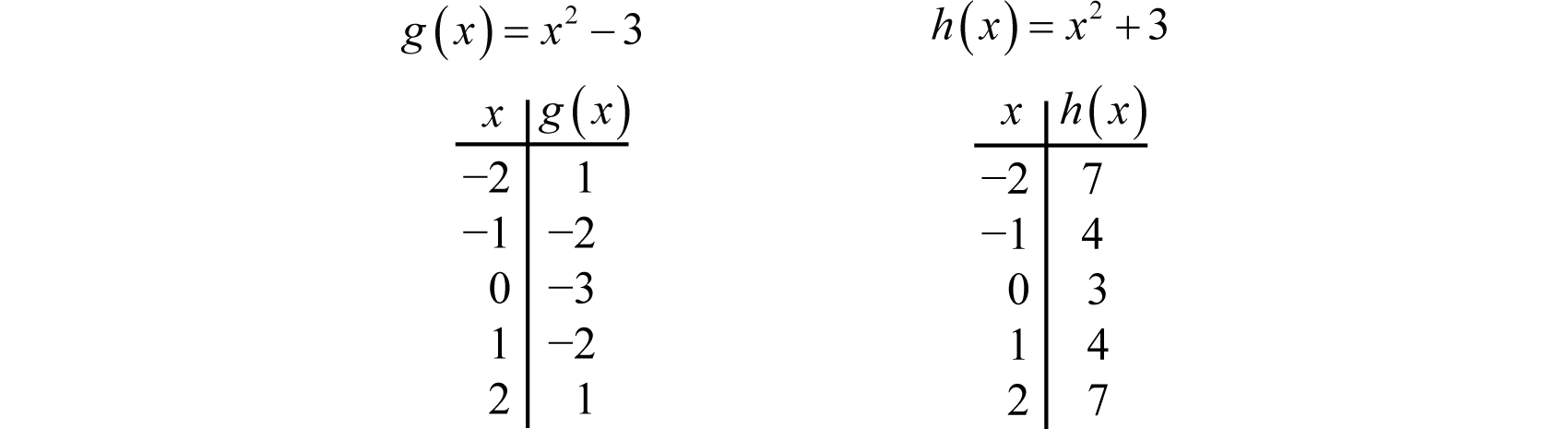



Using Transformations To Graph Functions




How Do You Find F X Using The Limit Definition Given F X X 2 1 2x 3 Socratic
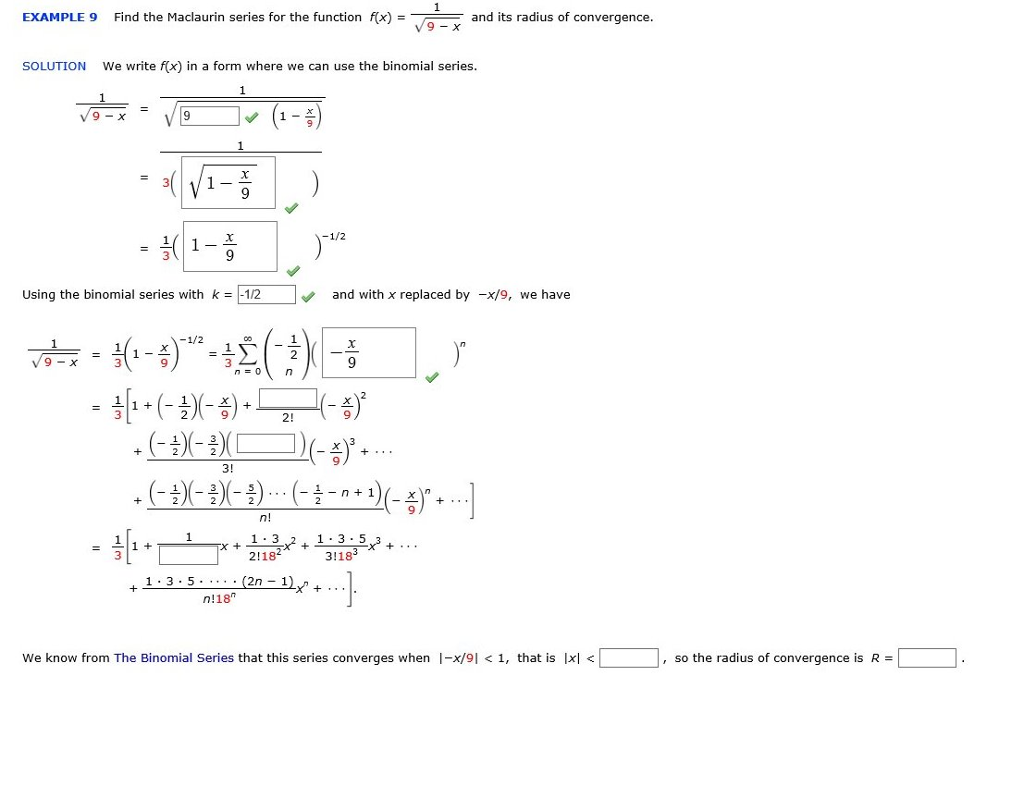



Solved Find The Maclaurin Series For The Function F X Chegg Com
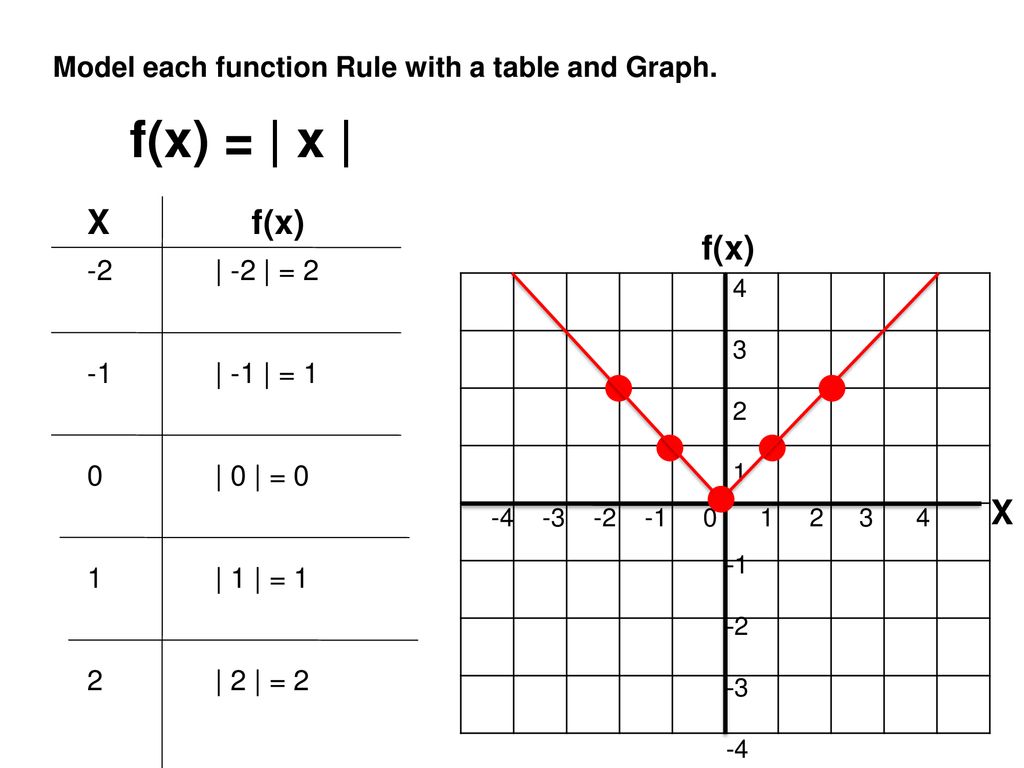



4 16 3 5 2 13 3 4 1 12 3 2 9 2 7 Ppt Download




If The Function F X X 2 1 X 1 When X 1 K When X 1




How To Prove That F X Ln X 2 1 Is Not Uniform Continuous Mathematics Stack Exchange




Ex 13 1 31 If Function F X Lim X 1 F X 2 X2 1 Pi




Let F X 1 2x 2 3x 1 Then Find The Value Of F X 2




Which Of The Following Represents Graph Of F X 1 2 X Brainly Com




Finding Inverse Functions Quadratic Example 2 Video Khan Academy




Solved If F X X And G X 1 Then F G X What Is Chegg Com




Show That The Function F X X 1 If X 2 2x 3




Answered 3 3x 1 34 F 33 F X 5x X2 36 Bartleby
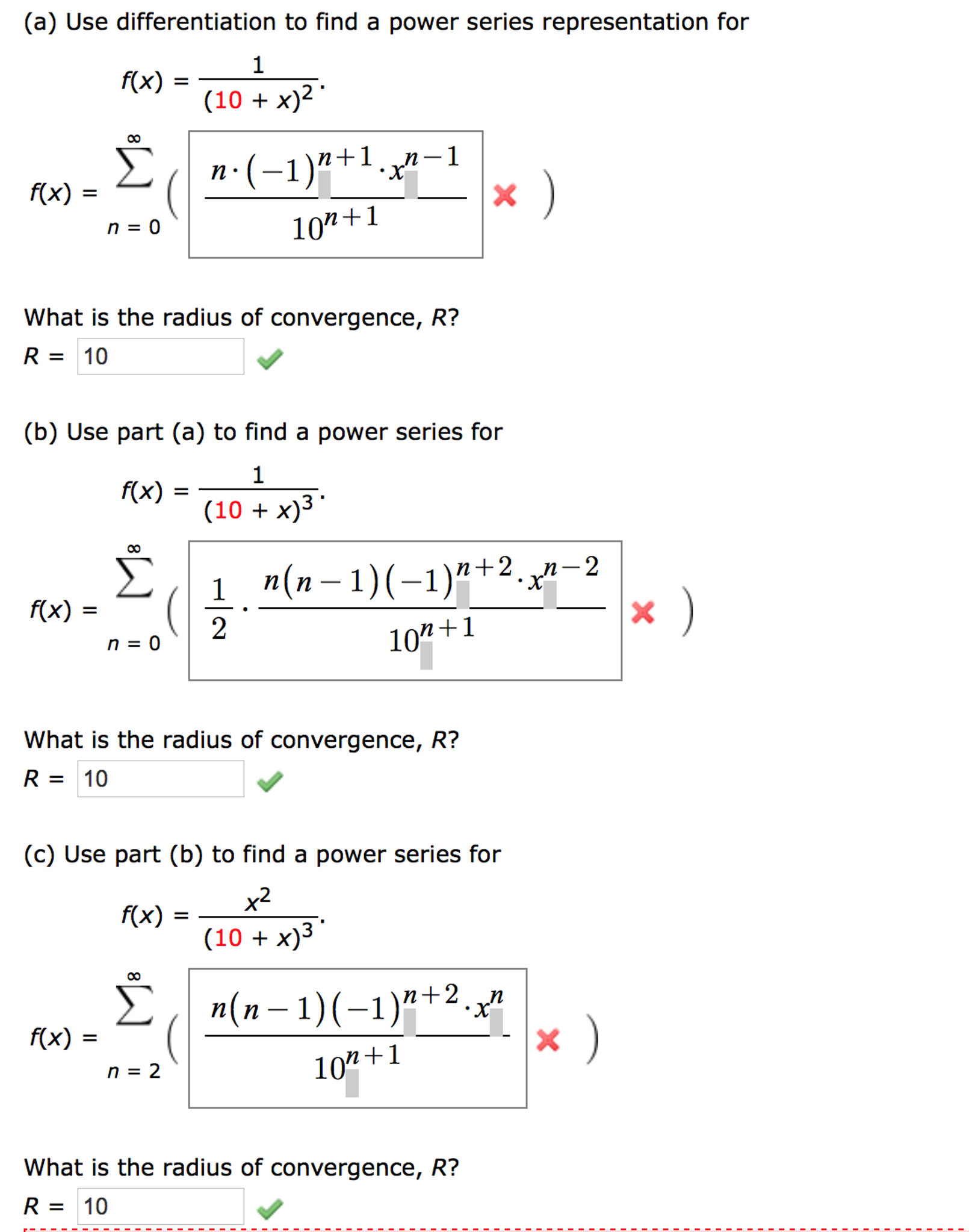



Use Differentiation To Find A Power Series Chegg Com




Maximum Value Of Function F X Frac X 4 X 2 X 6 2x 3 1 When X 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange




If F X X 1 4 X 2 3 X 3 2 X 4 Then The Value Of F
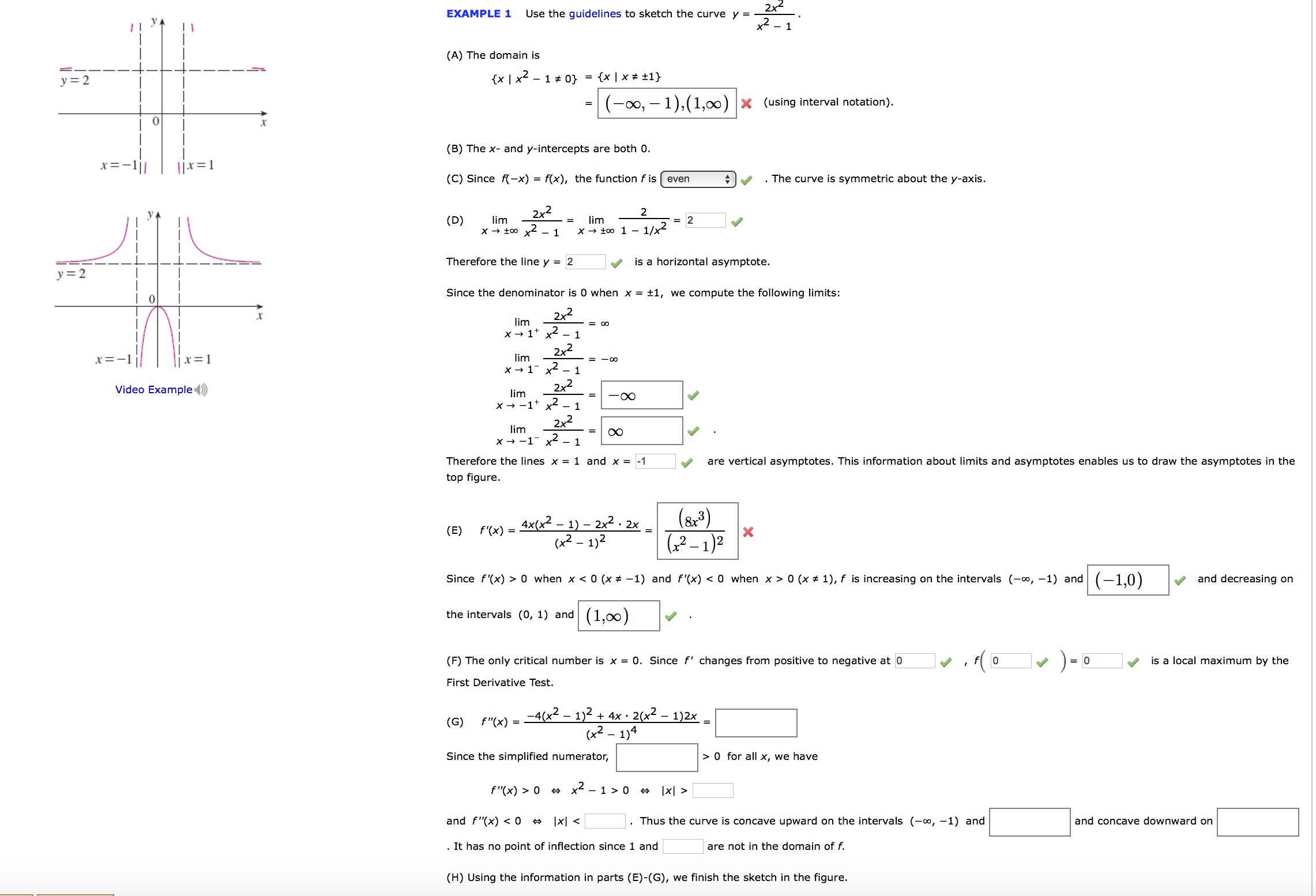



Use The Guidelines To Sketch The Curve Y 2x 2 X 2 Chegg Com



Answered V4 3x 14 F X 12 15 F X Sin 16 Bartleby




Number Of Critical Points Of The Function F X X 2 2 3 2x 1 Is Equal To



What Is The Domain And Range Of F X X 1 X 2 1 X 3 Quora




If F 2 X F 1 X 1 X X 3 X 1 1 And F X 0 Then Find




If F X Be Defined On 2 2 And Is Given By F X 1 2 X 0 X 1 0 X 2 And G X F X F X Find G X



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 2x 1 G X 3x 3 Socratic




Example 10 Discuss Continuity F X X 2 If X 1 X 2 If X 1




The Graph Of F X X 2 Is Shown Use The Parabola Tool To Graph G X 9 X 1 X 2 2graph The Brainly Com




If F X 2x 1 If X Gt 1 And X 2 1 If 1 Lt X Lt 1 And If F 1 F 3 F X F 2 F Youtube
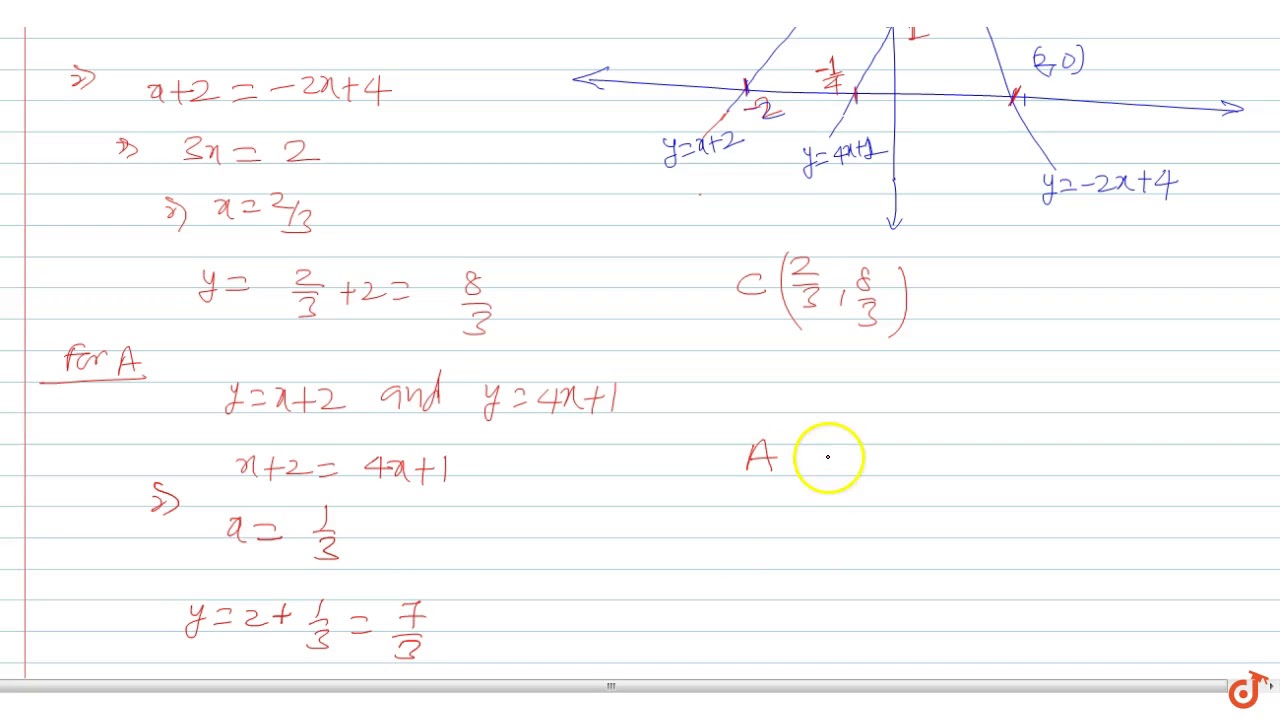



Let F X Min 4x 1 X 2 2x 4 Then The Maximum Value Of F X Is Youtube




Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X 1 2 F X Brainly Com
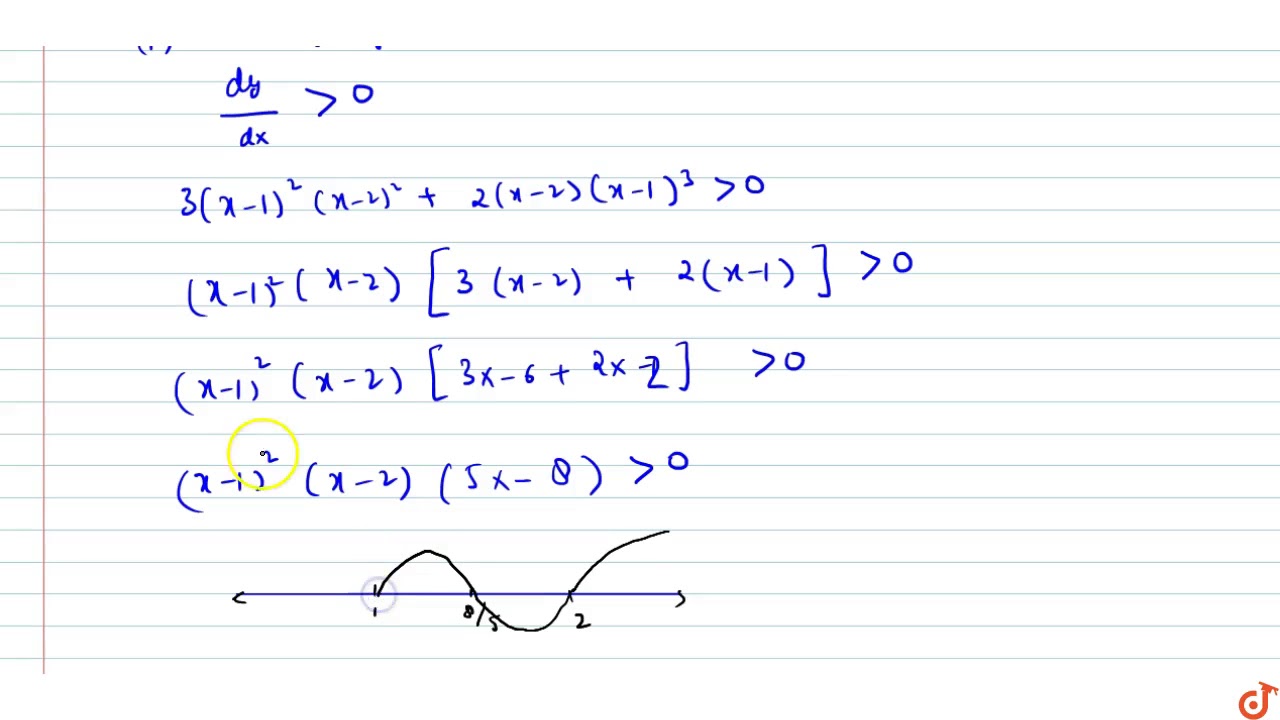



Find The Intervals In Which F X X 1 3 X 2 2 Is Increasing Or Decreasing Youtube
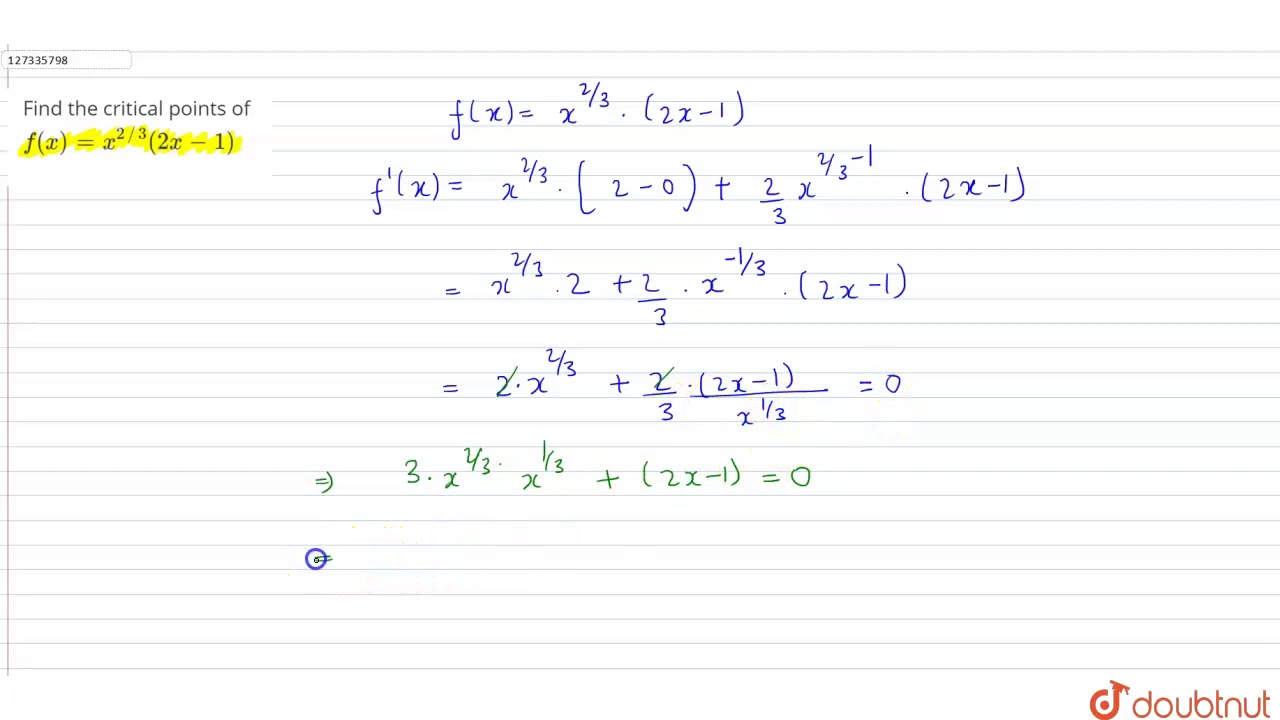



Find The Critical Points Of F X X 2 3 2x 1 Youtube




Q 104 If F X Then The Value Of F 1 F1 1 1 F2 1 2 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




If A 1 2 2 1 And F X 1 X 1 X Then F A Is




The Function F X X2 Is Graphed Above Which Of The Graphs Below Represents The Function G X X Brainly Com




Let F X 1 X 0 X 2 3 X 2 Lt X 3 Then Find Fof Fof Means Brainly In
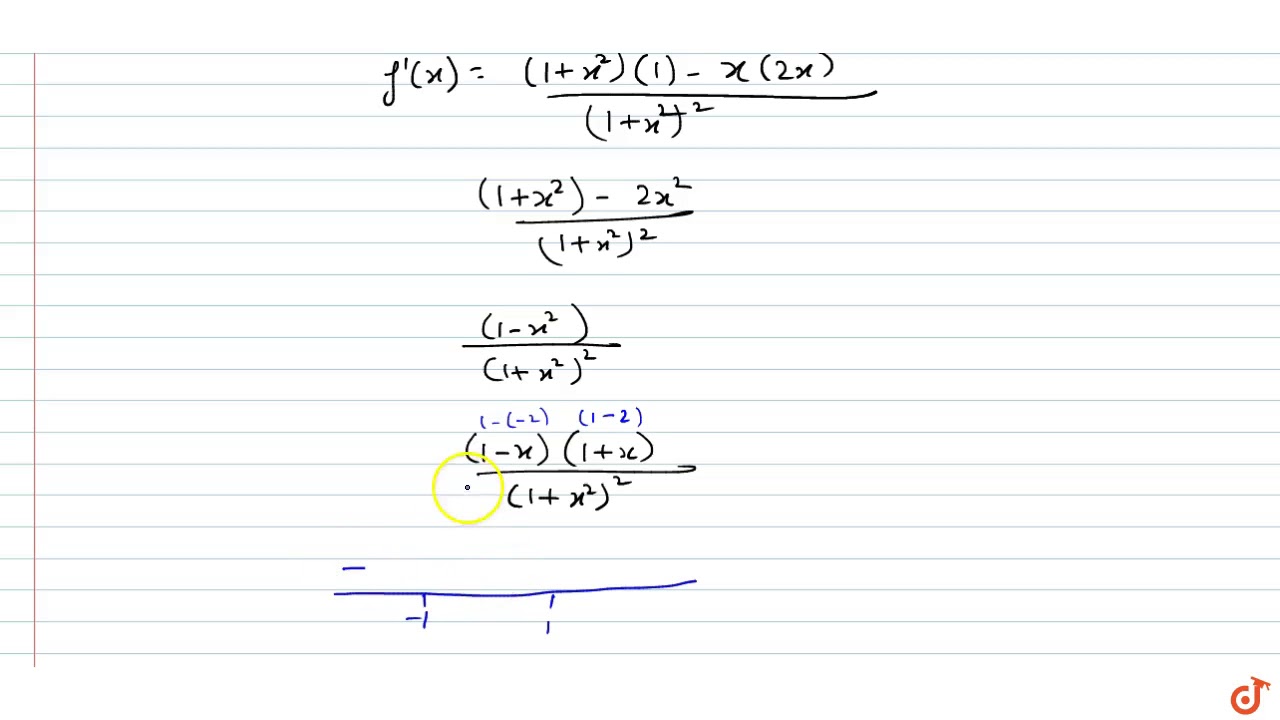



The Function F R Gt 1 2 1 2 Defined As F X X 1 X 2 Is Youtube




Let F X 1 X On 1 3 Find L F P And U F P When P 1 2 3 Mathematics Stack Exchange
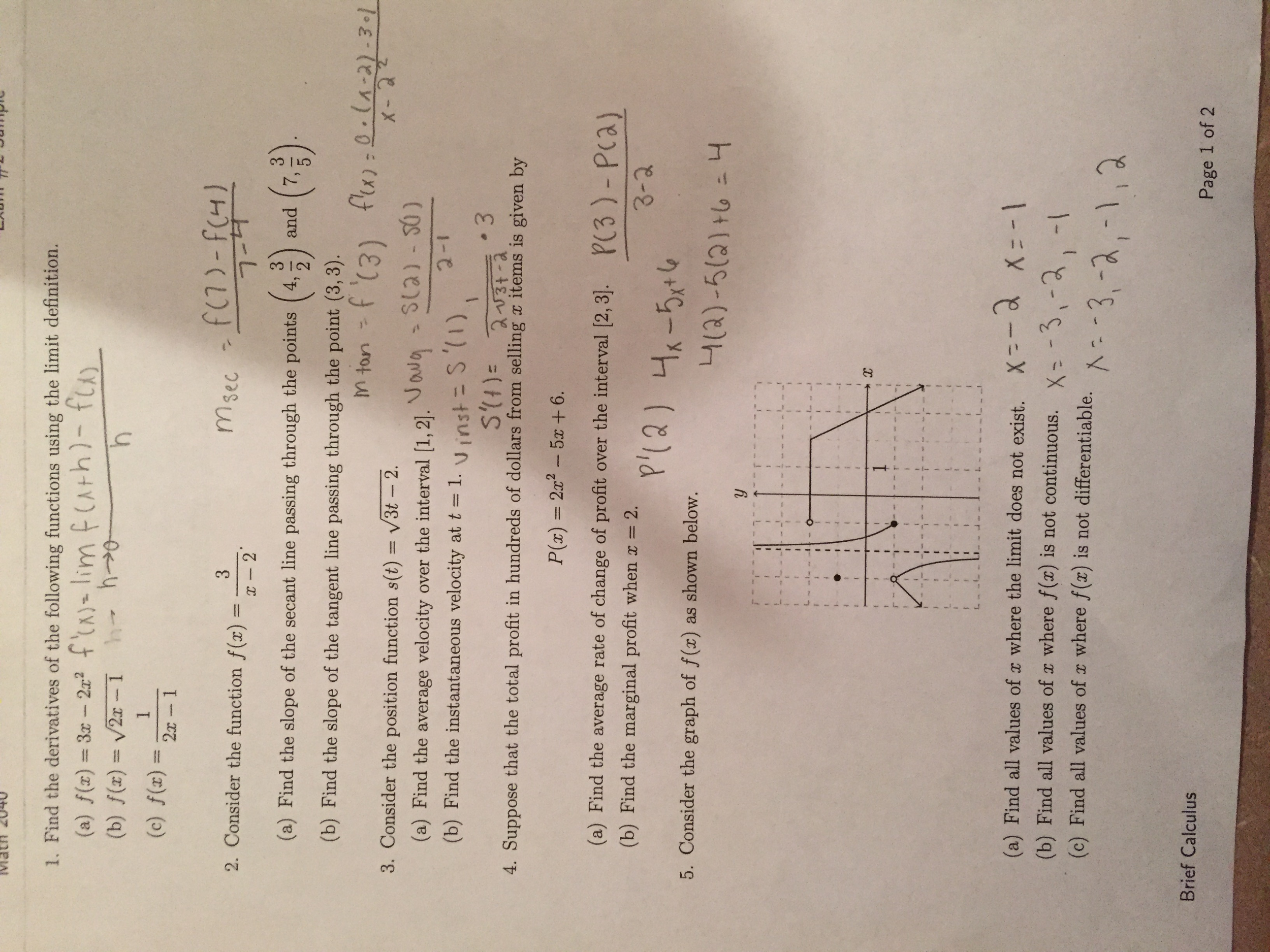



Solved Find The Derivatives Of The Following Functions Us Chegg Com




Find The Taylor Series Expansion For F X 1 X At X 2 Youtube




Ex 5 5 16 Find Derivative Of F X 1 X 1 X2 1 X4 1 X8



Bellwork Graph Each Line 1 3x Y 6 2 Y 1 2 X 3 Y Ppt Video Online Download




Derivative Of F X X 2 1 X 3 1 Using The Product Rule Youtube




If The Function F R R Defined By F X 4 X4 X 2 Then Show That F 1 X 1 F X And Hence Deduce The Value Of F 14 2f 12 F 34




Find The Derivative Of The Function Given By F X 1 X 1 X 2 1




Write The Value Of The Derivative Of F X X 1 X 3 At X 2 Youtube
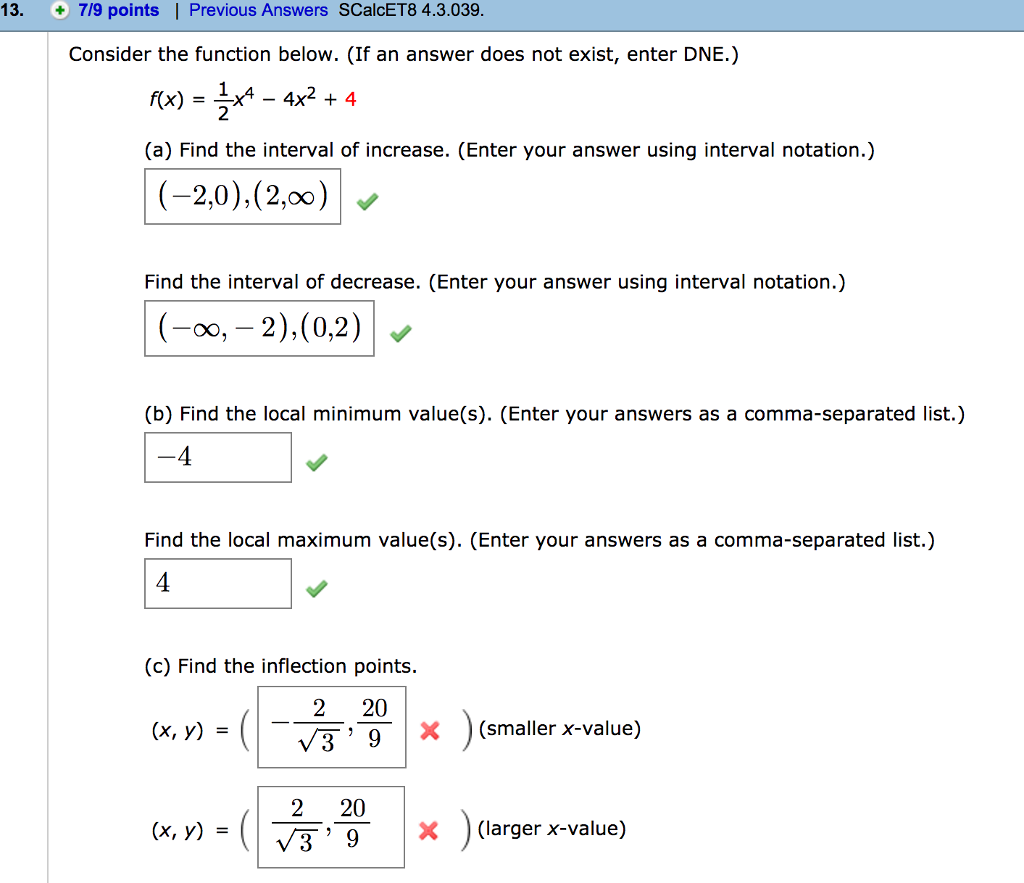



Consider The Function Below If An Answer Does Not Chegg Com
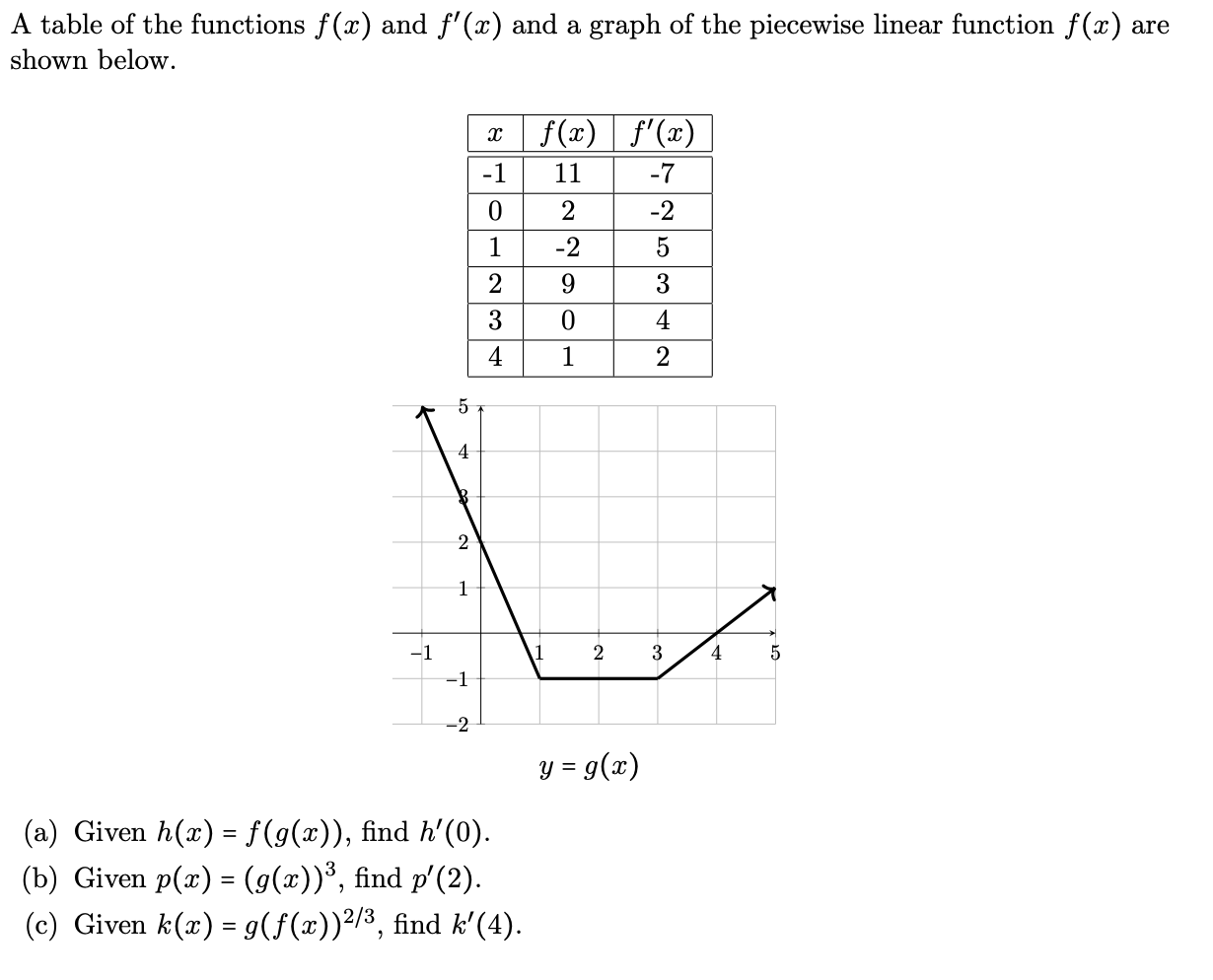



A Table Of The Functions F X And F X And A Graph Chegg Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿